New publication in “Journal of Computational Science”
6 May 2024See full article/ Veure l’article complet
English:
Improvement of the air quality in highly polluted cities is a challenge for today’s society. Many of the strategies that have been proposed for this purpose promote the creation of green infrastructures. The Weather Research and Forecasting model coupled with chemistry (WRF-Chem) is used to analyze the behavior of the most common pollutants and how they are dispersed as a result of different meteorological conditions. To also consider the impact of including green infrastructures on urban morphology, the BEP/BEM (Building Effect Parameterization/Building Energy Model) multi-layer urban scheme is also included in the system. Using the city of Barcelona as a case study, this paper confirms that the modeling methodology used up to now needs to be reviewed for the design of green cities. Certain limitations of the WRF-Chem+BEP/BEM coupled model when applied in urban resolution are discussed, as well as the reasons for such limitations, being the main contribution of this paper to show that an alternative paradigm such as Machine Learning techniques should be considered to address this challenge.
Català:
Millorar la qualitat de l’aire en ciutats altament contaminades és un repte per a la societat actual. Moltes de les estratègies que s’han proposat per a aquest propòsit promouen la creació d’infraestructures verdes. El model “Weather Research and Forecasting” acoplat amb química (WRF-Chem) s’utilitza per analitzar el comportament dels contaminants més comuns i la seva dispersió com a resultat de diferents condicions meteorològiques. Per a considerar també l’impacte de la inclusió d’infraestructures verdes en la morfologia urbana, s’inclou també l’esquema urbà multicapa “Building Effect Parameterization/ Building Energy Model” (BEP/BEM) en el sistema. Utilitzant la ciutat de Barcelona com a cas d’estudi, aquest article confirma que la metodologia de modelització utilitzada fins ara necessita ser revisada per al disseny de ciutats verdes. Es discuteixen certes limitacions del model acoblat WRF-Chem+BEP/BEM quan s’aplica en resolució urbana, així com les raons d’aquestes limitacions, sent la principal contribució d’aquest article mostrar que s’hauria de considerar un paradigma alternatiu com “Machine Learning” per abordar aquest repte.
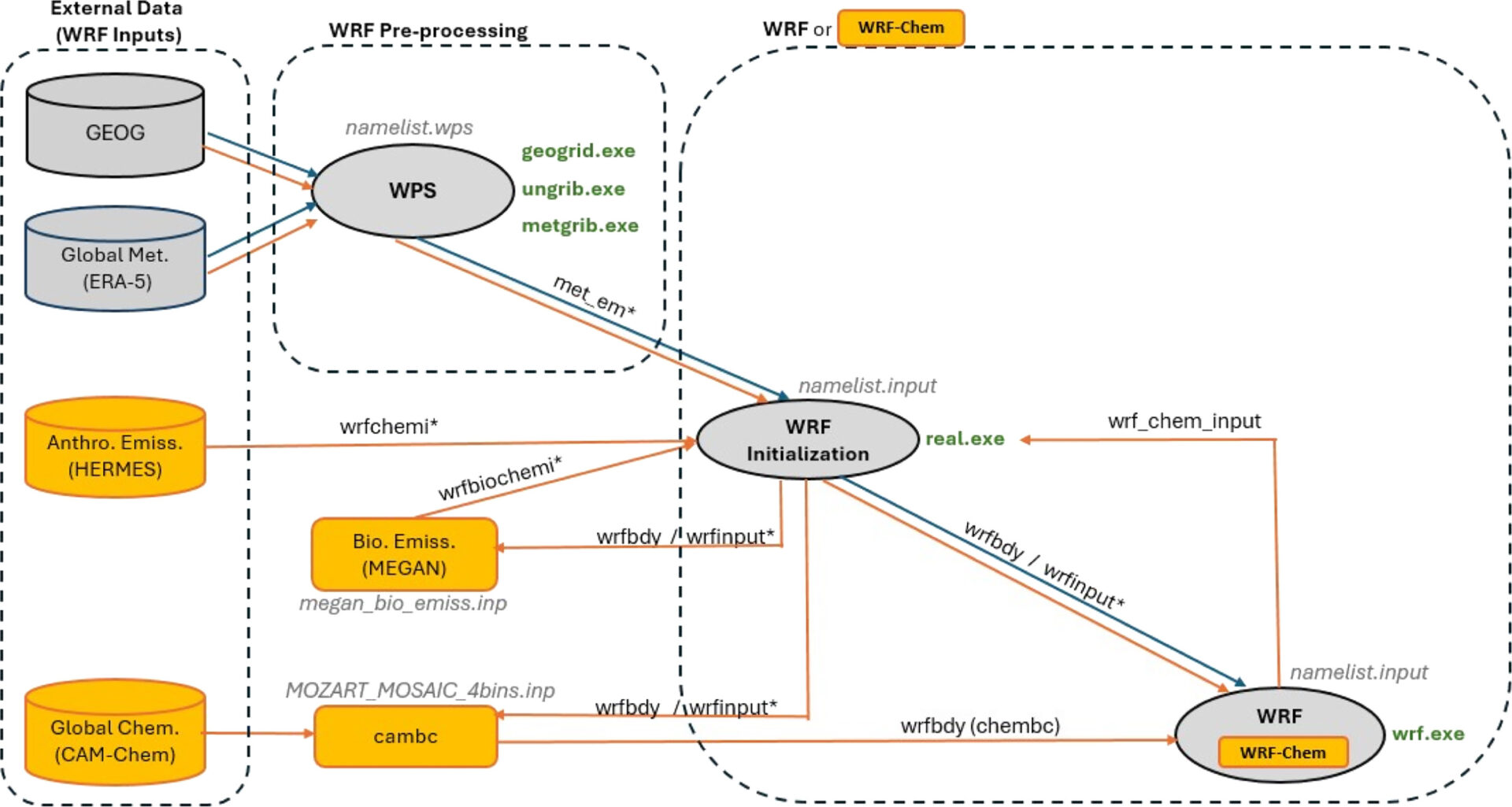
Figure: Execution scheme: WRF (+BEP/BEM) depicted by blue arrows, and WRF-Chem (+BEP/BEM) represented by orange arrows.